Table of Contents
ToggleIn the world of handheld gaming, the Game Boy reigns supreme as a nostalgic titan. But what makes this little device tick? Enter the Game Boy CPU, the unsung hero behind those pixelated adventures and catchy soundtracks. It’s like the wizard pulling the strings in a magical realm, only instead of spells, it conjures up some seriously addictive gameplay.
Imagine a tiny brain working tirelessly to deliver epic battles, puzzling challenges, and unforgettable moments—all while fitting snugly in your pocket. The Game Boy CPU isn’t just a piece of silicon; it’s the heart of a gaming revolution that turned casual gamers into lifelong fans. So buckle up as we dive into the fascinating world of this iconic CPU, where nostalgia meets tech wizardry in the most delightful way possible.
Overview of Game Boy CPU
The Game Boy CPU, known as the Sharp LR35902, serves as the heart of the device’s performance. This 8-bit microprocessor operates at a clock speed of 4.19 MHz, effectively managing game operations, graphics rendering, and sound processing. Developers relied on its capabilities to create engaging titles that defined handheld gaming.
With a combination of features from both the Z80 and Intel 8080 architectures, the CPU supports 8-bit instructions, providing versatility for software developers. It can address up to 64 KB of memory, which includes game data and runtime processes. Such design choices facilitated the memorable gameplay experiences that captivated millions.
Memory is organized into various types, including ROM, RAM, and video RAM. The ROM chip typically hosts game cartridges while SRAM allows for temporary data storage during gameplay. Significant in its functionality, the CPU collaborates closely with the Game Boy’s GPU to render the iconic, pixelated graphics that users cherish.
Programming the Game Boy CPU involves using assembly language, optimizing performance, and making the most out of limited resources. Game developers pushed the boundaries of creativity within the hardware’s constraints, enabling complex gameplay mechanics and compelling narratives. Each title exemplified how the CPU’s architecture unlocked new gaming possibilities.
In short, the Game Boy CPU played an essential role in transforming gaming, influencing subsequent handheld devices. Its legacy remains evident in today’s gaming technology, showcasing how innovative CPU design can impact user experience and engagement.
Architecture of Game Boy CPU
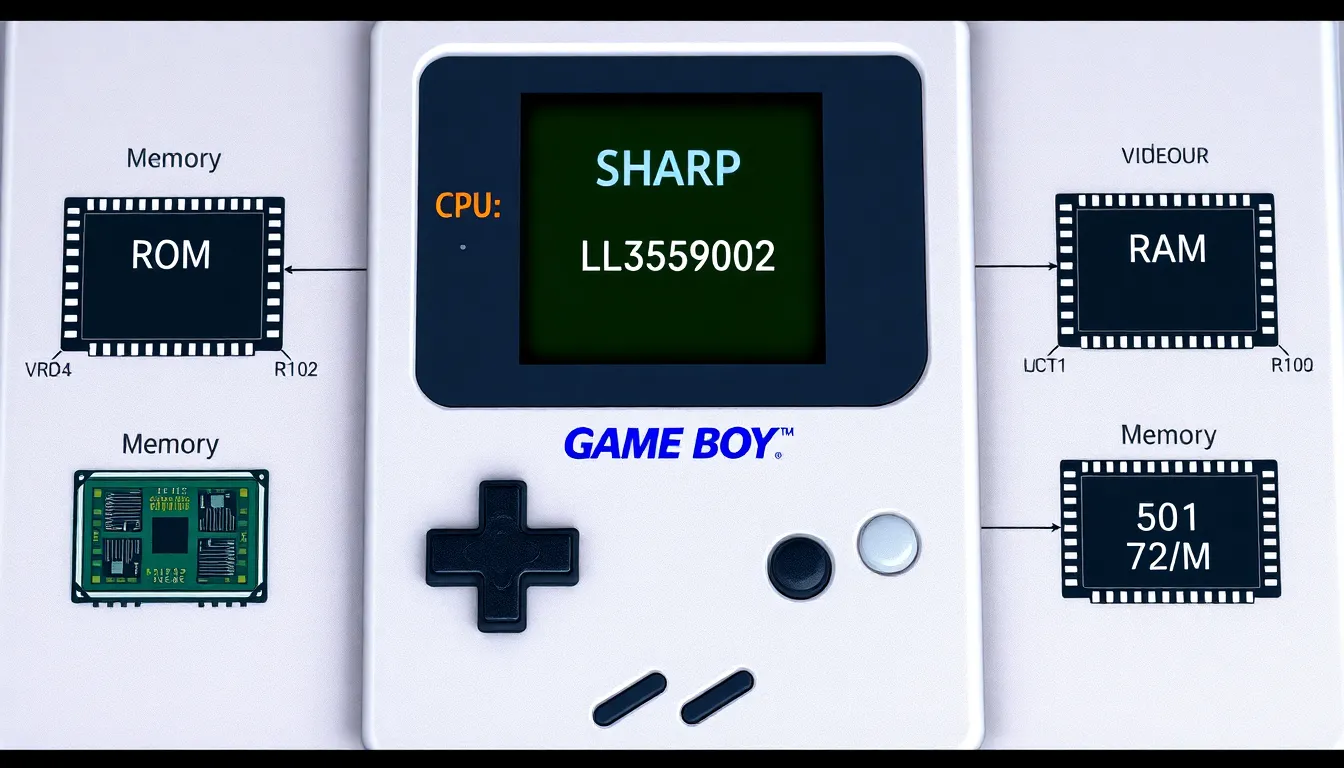
The architecture of the Game Boy CPU highlights its unique blend of features. This design delivers a solid gaming experience for players.
Central Processing Unit Features
The Game Boy CPU operates using the Sharp LR35902, an 8-bit microprocessor. Featuring a clock speed of 4.19 MHz, it executes tasks efficiently. It supports 8-bit instruction sets, enabling straightforward programming for developers. Game operation management, graphics rendering, and sound processing are seamlessly handled. Combining characteristics from both the Z80 and Intel 8080, this CPU stands out in handheld gaming history. The efficiency in executing complex tasks proves vital for the immersive experiences that players cherish.
Memory Management
Memory management within the Game Boy architecture integrates multiple memory types. Up to 64 KB of memory gets addressed by the CPU, which includes ROM, RAM, and video RAM. Each memory type serves a specific purpose in gameplay and graphics rendering. ROM stores the game data, while RAM allows for temporary data manipulation. Video RAM maintains graphical data for the display. Effective collaboration between the CPU and memory types enhances gaming performance. Overall, efficient memory management contributes significantly to the nostalgic enjoyment of classic titles, shaping a memorable gaming landscape.
Performance Analysis
The Game Boy CPU delivers impressive performance, contributing significantly to the handheld gaming experience. Analysis of its critical components reveal key factors influencing overall functionality.
Processing Speed
Operating at a clock speed of 4.19 MHz, the Sharp LR35902 efficiently manages game processing tasks. This speed enables rapid execution of game logic and delivery of smooth graphics. Games utilizing simple mechanics benefit from higher processing efficiency. Complex titles still perform well due to effective CPU architecture, which integrates Z80 and Intel 8080 features. Developers leverage assembly language to optimize operations, ensuring responsiveness in gameplay experiences.
Power Consumption
Power efficiency is a hallmark of the Game Boy CPU, crucial for extending battery life. At a mere 5 volts, the system minimizes energy expenditure while delivering performance. Comparatively, no other contemporaneous hardware rivals its balance of power and performance. This efficiency allows players to enjoy extended gaming sessions without frequent battery replacements. The design philosophy prioritizes longevity, making the Game Boy an enduring member of gaming history.
Comparisons with Other Handheld Consoles
The Game Boy CPU stands out among handheld consoles due to its unique architecture and efficient performance. While comparing it to the Nintendo Switch, the Game Boy’s Sharp LR35902 processor operates at 4.19 MHz, significantly lower than the Switch’s custom NVIDIA chipset. This difference in processing power affects graphical capabilities and game complexity, though the Game Boy thrived on simplicity, creating beloved classics.
In contrast, the Sega Game Gear features a 16-bit Zilog Z80 processor. This CPU operates at a faster clock speed of 3.58 MHz, but lacks the power efficiency found in the Game Boy. The Game Gear consumes more battery power, limiting playtime compared to the Game Boy’s longer-lasting gaming experience.
Another competitor, the Atari Lynx, utilizes a custom 16-bit CPU. This CPU offers superior graphics, yet requires more resources. Battery life suffers with the Lynx, making it less practical for extended gameplay.
Sony’s PSP showcases advanced technology with a 333 MHz MIPS processor, elevating graphical performance and complex game design. However, the PSP’s increased processing demands lead to shorter battery life, a stark contrast to the power management of the Game Boy.
Different handheld systems target varied gaming experiences. The Game Boy embraces nostalgia, simplicity, and efficiency, solidifying its legacy in gaming history. Other consoles highlight enhanced graphics and processing power, but the Game Boy’s performance proves sufficient for enjoyable gameplay. Each console’s unique approach to CPU design shapes player experiences, leading to diverse preferences in handheld gaming.
Impact on Game Development
Game development for the Game Boy thrived due to the capabilities of its CPU. The Sharp LR35902 microprocessor’s efficient architecture allowed developers to create engaging gameplay experiences within hardware limitations. Its combination of Z80 and Intel 8080 features simplified programming, enabling the creation of innovative titles that captivated audiences.
Developers utilized assembly language to extract the maximum performance from the CPU. This programming language provided control over system resources, leading to games that featured intricate mechanics and memorable graphics. Titles like “The Legend of Zelda: Link’s Awakening” demonstrated how creativity flourished when leveraging the processing power of the Game Boy CPU.
Memory organization further influenced game development. With ROM storing critical game data and RAM supporting dynamic data manipulation, developers ensured smooth gameplay. Video RAM played a vital role in rendering pixelated graphics that became iconic. This efficient collaboration allowed for detailed environments and immersive experiences.
Optimizing performance was crucial in maximizing engagement. Despite operating at 4.19 MHz, the CPU handled complex tasks with finesse. Responding quickly to player input became a hallmark of beloved games, enhancing overall user satisfaction. Battery efficiency at just 5 volts directly impacted the gaming experience, prolonging sessions and encouraging exploration of game worlds.
Comparisons with other handheld consoles highlight the Game Boy’s unique advantages. Although modern systems champion graphics and speed, the Game Boy’s simplicity and nostalgia fostered deep connections with players. Titles from the Game Boy era continue to influence current game design strategies, demonstrating the importance of aligning technology with creative vision.
The Game Boy CPU remains a pivotal element in the handheld gaming landscape. Its innovative design and efficient architecture not only shaped the gaming experiences of its time but also laid the groundwork for future developments. By balancing performance and power efficiency, it enabled countless memorable titles that continue to resonate with gamers today.
As technology evolves, the legacy of the Game Boy CPU endures, reminding players of the charm and simplicity that defined an era. Its influence can still be seen in modern game design, showcasing the lasting impact of a well-crafted microprocessor on the gaming industry. The Game Boy will forever be celebrated as a cornerstone of handheld gaming history.







